5 Super Healthy Foods that Will Help Force Epic Muscle Growth Faster – BOXROX
Building muscle is a science that goes beyond mere exercise; it involves a strategic approach to nutrition. The right foods can supercharge your muscle growth, improving both size and strength. Here, we delve into five super healthy foods that are scientifically proven to enhance muscle growth effectively.
1. Lean Beef
Nutrient Profile and Benefits
Lean beef is an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for muscle repair and growth. It is rich in amino acids, particularly leucine, which plays a critical role in muscle protein synthesis. Additionally, lean beef provides creatine, iron, and B-vitamins, all of which contribute to improved muscle performance and recovery.

Scientific Evidence
A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that consuming lean beef post-exercise led to significant improvements in muscle protein synthesis compared to other protein sources . Another study highlighted that the high levels of leucine in beef are particularly effective in promoting muscle hypertrophy and recovery.
How to Incorporate Lean Beef
For optimal benefits, include lean beef in your diet at least three times a week. Opt for cuts like sirloin, tenderloin, or 95% lean ground beef. Pair it with complex carbohydrates and vegetables for a balanced meal.

2. Eggs
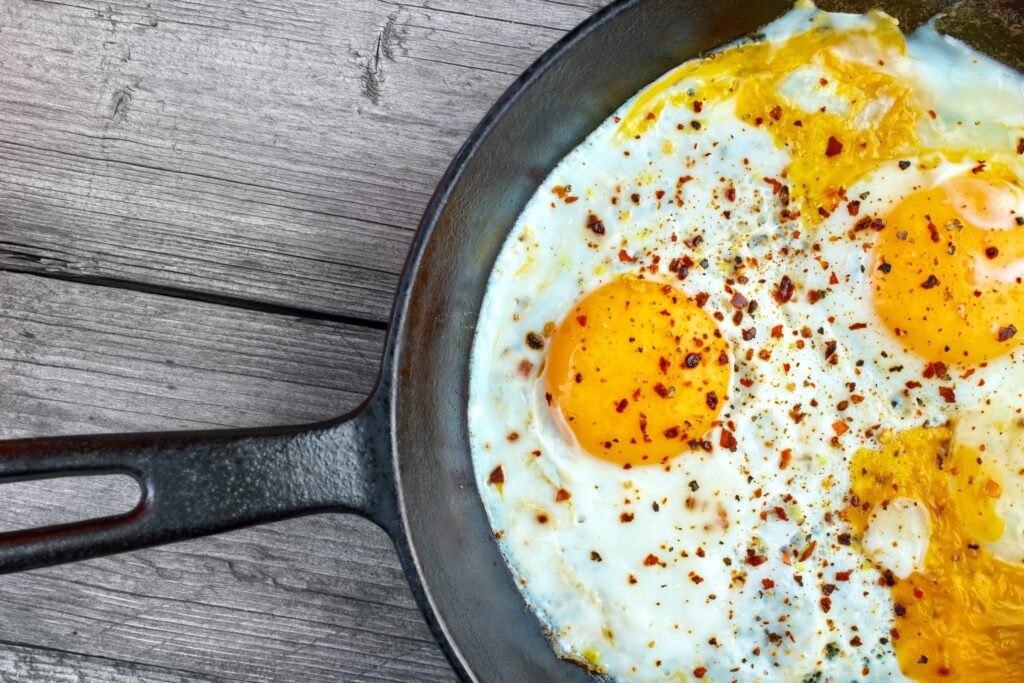

Nutrient Profile and Benefits
Eggs are often dubbed the “perfect protein” due to their complete amino acid profile. Each egg contains around 6 grams of high-quality protein along with vitamins and minerals such as vitamin B12, riboflavin, and selenium. The yolk also provides healthy fats and additional nutrients that support muscle growth.
Scientific Evidence
Research in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition indicates that whole eggs are more effective in stimulating muscle protein synthesis than egg whites alone. The study suggests that the combination of protein and fats in whole eggs enhances the anabolic response to resistance training.
How to Incorporate Eggs
Include eggs in your breakfast or as a post-workout meal. Aim for three to four whole eggs daily, depending on your dietary needs and cholesterol levels. Combine eggs with vegetables or whole grains for a nutrient-dense meal.

3. Greek Yogurt

Nutrient Profile and Benefits
Greek yogurt is a protein powerhouse, containing approximately 10 grams of protein per 100 grams. It is also a good source of calcium, probiotics, and vitamin D. The high casein content in Greek yogurt provides a slow-release protein that can sustain muscle protein synthesis over several hours.

Scientific Evidence
A study in the British Journal of Nutrition found that consuming Greek yogurt before bed significantly increased overnight muscle protein synthesis compared to a placebo. This slow-digesting protein source ensures that muscles receive a steady supply of amino acids during sleep, enhancing recovery and growth.
How to Incorporate Greek Yogurt
Eat Greek yogurt as a snack, post-workout meal, or part of your breakfast. Pair it with fruits, nuts, or honey to enhance its nutritional profile. Aim for one to two servings per day.
4. Salmon
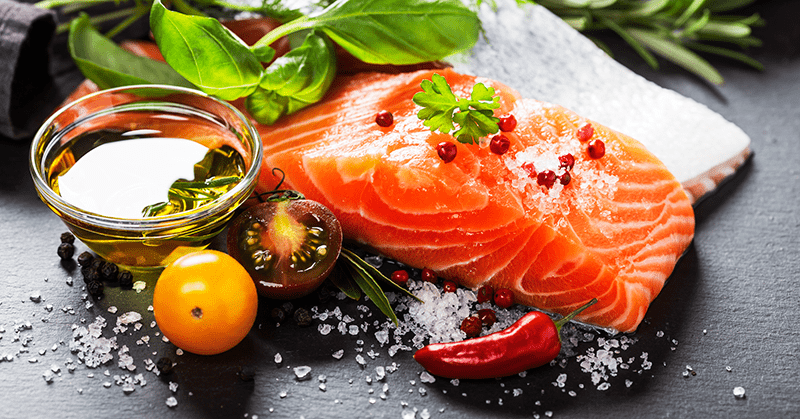

Nutrient Profile and Benefits
Salmon is not only rich in high-quality protein but also packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties. These fats help reduce muscle soreness and improve recovery. Additionally, salmon provides essential nutrients like vitamin D, selenium, and B vitamins.
Scientific Evidence
Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that omega-3 fatty acids in salmon enhance muscle protein synthesis and promote muscle growth. Another study found that regular consumption of fatty fish like salmon reduced exercise-induced muscle damage and inflammation .
How to Incorporate Salmon
Include salmon in your diet at least twice a week. Opt for grilled, baked, or poached salmon to retain its nutrient profile. Combine it with leafy greens and whole grains for a balanced meal.
5. Quinoa
Nutrient Profile and Benefits
Quinoa is a complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids, which makes it an excellent plant-based protein source. It is also rich in complex carbohydrates, fiber, magnesium, iron, and B-vitamins, providing a comprehensive nutrient profile that supports muscle growth and overall health.
Scientific Evidence
A study in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition highlighted that quinoa’s complete amino acid profile and high magnesium content make it an effective food for muscle hypertrophy and recovery. Magnesium plays a crucial role in muscle contractions and energy production, enhancing workout performance.
How to Incorporate Quinoa
Use quinoa as a base for salads, bowls, or as a side dish. Aim for one cup of cooked quinoa per meal, combining it with other protein sources and vegetables for a nutrient-dense meal. Consuming quinoa post-workout can help replenish glycogen stores and aid muscle recovery.
Conclusion
Incorporating these five superfoods into your diet can significantly enhance muscle growth and recovery. Each of these foods offers a unique set of nutrients that support muscle protein synthesis, reduce inflammation, and improve overall performance. To achieve the best results, ensure a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein sources, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. Pairing these dietary strategies with a consistent workout regimen will help you achieve epic muscle growth faster.
Key Takeaways
| Food | Key Benefits | How to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Lean Beef | High-quality protein, creatine, iron, B-vitamins | Include 3 times a week with complex carbs |
| Eggs | Complete protein, vitamins, and healthy fats | 3-4 whole eggs daily, combined with vegetables |
| Greek Yogurt | High in protein, slow-release casein, probiotics, calcium | 1-2 servings per day as a snack or post-workout |
| Salmon | High-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, selenium | Include 2 times a week with leafy greens |
| Quinoa | Complete protein, complex carbs, fiber, magnesium | 1 cup cooked per meal, post-workout |
References
- Symons, T.B., Sheffield-Moore, M., Wolfe, R.R. and Paddon-Jones, D., 2009. “A moderate serving of high-quality protein maximally stimulates skeletal muscle protein synthesis in young and elderly subjects.” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89(1), pp.161-168.
- Phillips, S.M., 2012. “Dietary protein requirements and adaptive advantages in athletes.” British Journal of Nutrition, 108(S2), pp.S158-S167.
- van Vliet, S., Shy, E.L., Abou Sawan, S., Beals, J.W., West, D.W.D., Skinner, S.K. and Burd, N.A., 2017. “Consumption of whole eggs promotes greater stimulation of postexercise muscle protein synthesis than consumption of isonitrogenous amounts of egg whites in young men.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1), p.17.
- Snijders, T., Res, P.T., Smeets, J.S., van Vliet, S., van Kranenburg, J. and van Loon, L.J., 2015. “Protein ingestion before sleep improves postexercise overnight recovery.” British Journal of Nutrition, 114(8), pp.1406-1414.
- Smith, G.I., Atherton, P., Reeds, D.N., Mohammed, B.S., Rankin, D., Rennie, M.J. and Mittendorfer, B., 2011. “Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids augment the muscle protein anabolic response to hyperinsulinemia-hyperaminoacidemia in healthy young and middle-aged men and women.” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 93(2), pp.402-412.
- McGlory, C., Wardle, S.L., Macnaughton, L.S., Witard, O.C., Scott, E., Dick, J.R., Macdonald, I.A., Bell, J.G. and Tipton, K.D., 2016. “Fish oil supplementation suppresses resistance exercise and feeding-induced increases in anabolic signaling without affecting myofibrillar protein synthesis in young men.” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 104(2), pp.536-544.
- Tang, J.E., Moore, D.R., Kujbida, G.W., Tarnopolsky, M.A. and Phillips, S.M., 2009. “Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in young men.” Journal of Applied Physiology, 107(3), pp.987-992.




